Contents
OEDOGONIUM
CLASSIFICATION OF OEDOGONIUM
Sub-division :- Algae
Class :- Chlorophyceae
Order :- Oedogoniales
Family :- Oedogoniaceae
Genus :- Oedogonium

THALLUS OF OEDOGONIUM
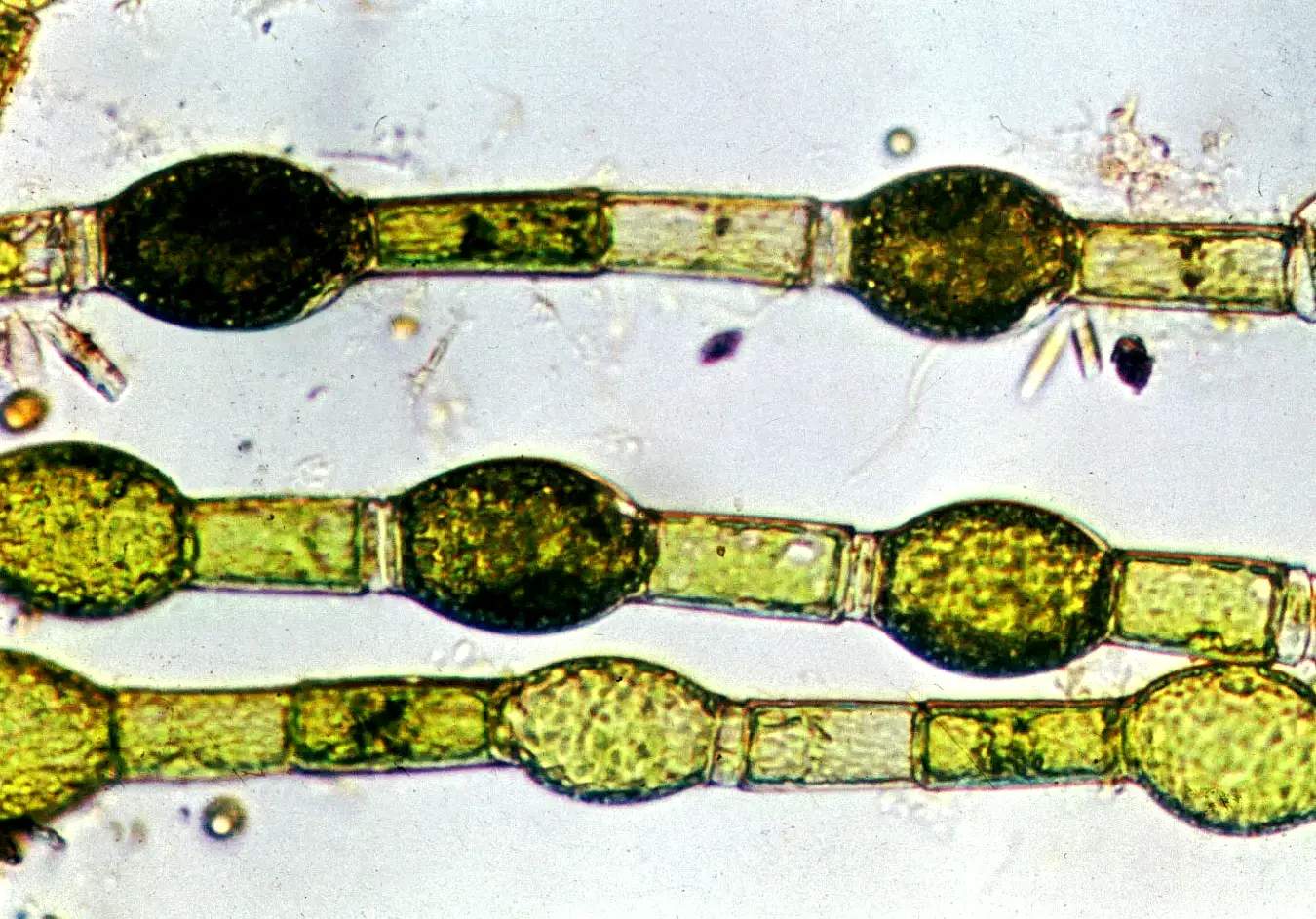
- Thallus is multicellular, filamentous and unbranched.
- A filament is differentiated into three types of cells according to their position :
- basal
- intercalary and
- apical.
- The basal cell of a filament functions as a holdfast. The lower part of the holdfast is either disc-like or finger-shaped. The upper part is mostly broad and rounded. The basal part of the cell generally lacks green pigment and, therefore, is non-green unlike other cells of the filament.
- A cell at the tip of the filament is known as’ apical cell. It is rounded at its free surface.
- The cells present between basal and the apical cells are intercalary cells. These show typical cell structure.
- The typical cell is cylindrical.
- Cell wall is thick and three layered.
- Inner to cell wall is a reticulate chloroplast that runs parallel to the long axis of the cell. Many pyrenoids are present in the chloroplast.
- The cell is uninucleate. The nucleus is situated near the cell wall and is held by thin and delicate cytoplasmic strands.
- Mature and old cells show ‘cap cells’ at their upper end. These are characteristic of the members of Oedogoniales.

OOGONIUM OF OEDOGONIUM
- Oogonia are intercalary or terminal in position.
- Oogonium may be solitary or occur in a row of 2-3 or even more.
- Oogonium generally shows one or more cap cells at its upper end, indicating its development from a comparatively older cell.
- It is mostly spherical or oval in shape and larger than a vegetative cell.
- At the base of each oogonium lies a small and flat daughter cell, known as supporting or suffultory cell.
- Oogonium encloses a single large ovum.
- The wall of the oogonium has a small pore on one side, Known as receptive pore.
- Just opposite the receptive pore, protoplast of the oogonium has a hyaline area-receptive spot.
- Uninucleate protoplast is rich in reserve food.

ANTHERIDIUM OF OEDOGONIUM
- Antheridia are mostly intercalary in position.
- Numerous antheridia form a long chain being arranged in a series.
- An antheridium is a small and flat cell.
- Each antheridium has two nuclei lying side by side, surrounded by dense cytoplasmic contents. Each of such protoplasmic groups later on metamorphoses into a multiflagellate antherozoid.

DWARF MALE OR NANNANDRIUM OF OEDOGONIUM
- The dwarf male (or nannandrium) is characteristic of nannandrous species.
- The dwarf male is produced by the germination of androspore.
- Androspores are formed inside the androsporangia.
- Androsporangia form a long chain of small and flat cells in intercalary position in the filament.
- Each androsporangium develops a single multiflagellate androspore (in contrast, per antheridium two antherozoids are produced).
- Androspore germinates to produce a dwarf male or nannandrium which remains attached either to the wall of the oogonium or to the suffultory cell.
- A dwarf male is made of a stalk cell and a terminal row of 2-3 cells.
- Stalk cell is at the base by which the dwarf male is attached to the filament. It has a disclike or finger-like structure at its base.
- The terminal row has 2-3 small, flat and narrow antheridia.
- Each anteridium has two multiflagellate antherozoids.
zygote of oedogonium
- Zygote is thick-walled post-fertilization structure. The wall is generally three layered.
- The layer outside the innermost may be smooth, ornamented or verrucose.
- Zygote develops red colour due to the accumulation of reserve food in the form of reddish oil drops.
IDENTIFICATION
- Sub-division– Algae
- Presence of a simple thallus.
- Chlorophyll present
- Cell wall made of cellulose.
- Class – Chlorophyceae
- Presence of a definite nucleus
- Chloroplast present. grass green colour
- Presence of starch
- Reproductive structure motile and flagella equal in length.
- Order – Oedogoniales
- Cells uninucleate, filaments branched or unbrahched,
- Cell division forming ‘caps’.
- Chloroplast reticulate
- Zoospores and antherozoids bear a whorl of flagella
- Production of dwarf males.
- Family – Oedogoniaceae (A single family)
- Genus – Oedogonium
- Filaments unbranched
- Cells cylindrical
- Holdfast well developed.

REFERENCES

Leave a Reply