Contents
HYDRODICTYON
CLASSIFICATION OF HYDRODICTYON
Sub-division :- Algae
Class :- Chlorophyceae
Order :- Chlorococcales
Family :- Hydrodictyaceae
Genus :- Hydrodictyon

GENERAL CHARATERSTICS OF HYDRODICTYON
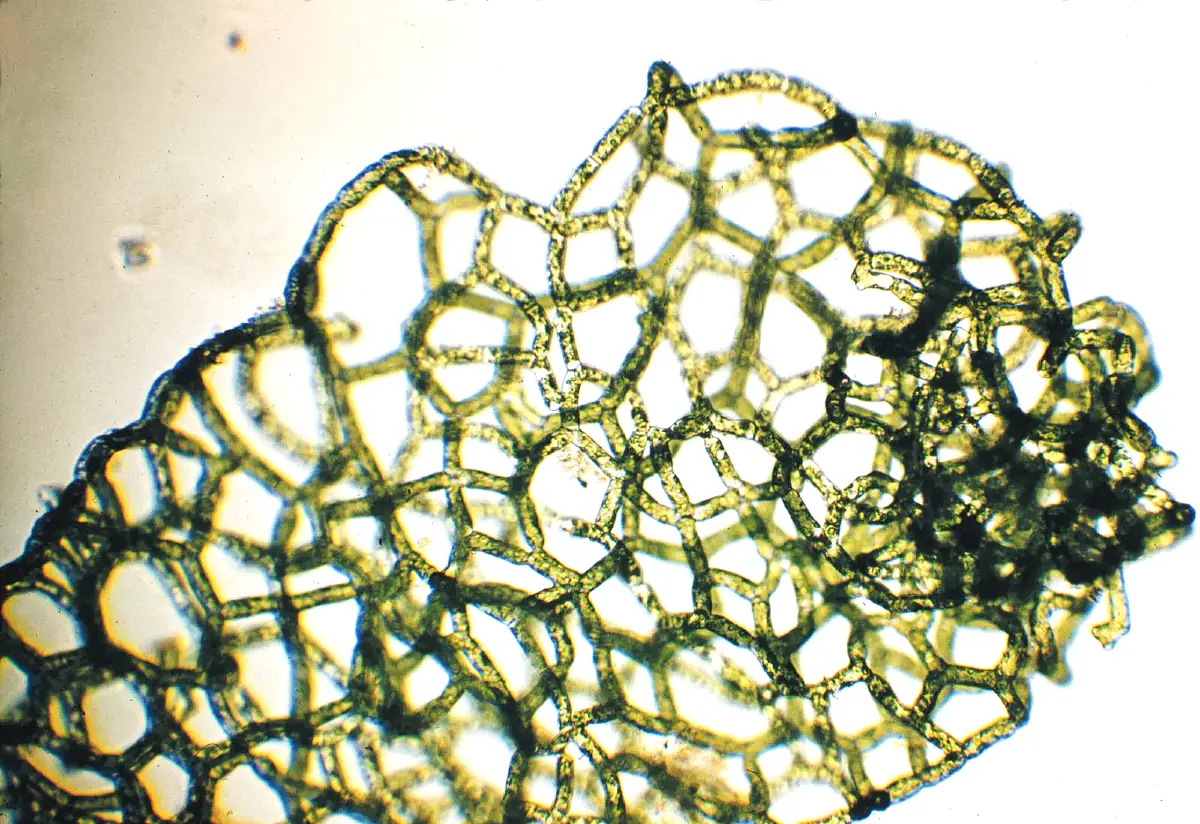
- The thallus is a multicellular colony forming a net-like structure.
- Colony is a hollow and sac-like or saucer-like (saccate), cylindrical network, closed at both the ends.
- The spaces of the reticulum are bound by five or six cells (this number varies between 3-10 cells) which form a pentagonal or hexagonal structure.
- The cells are cylindrical. End walls are angular to facilitate the formation of a mesh.
- A cell has a large central vacuole.
- Cytoplasm lies towards the periphery.
- Cells are multinucleate. The young cells are however, uninucleate.
- Cell is called a coenocyte because of its multinucleate nature and presence of large central vacuole.
- Young cells have zonate or entire chloroplast. Little mature cells possess reticulate chloroplast. However, during older stages chloroplast may assume discoid shape and diffuses throughout the cytoplasm.
- Chloroplast contains large number of pyrenoids.

IDENTIFICATION
- Sub-division– Algae
- Presence of a simple thallus.
- Chlorophyll present
- Cell wall made of cellulose.
- Class – Chlorophyceae
- Presence of a definite nucleus
- Chloroplast present. grass green colour
- Presence of starch
- Reproductive structure motile and flagella equal in length.
- Order – Chlorococcales
- Cells mostly single; if united form non filamentous colonies of definite shape and size
- Cells uni- or multinucleate
- Asexual reproduction by zoospores or autospores,
- Sexual reproduction isogamous.
- Family – Hydrodictyaceae
- Cells united to form coenobe
- Reproduction by zoospores and biflagellate gametes.
- Genus – Hydrodictyon
- Coenobe a saccate reticulum
- Chloroplast reticulate or discoid
- Uni- or multinucleate coenocytic cells.

REFERENCES

Leave a Reply