Contents
COLEOCHAETE
CLASSIFICATION OF COLEOCHAETE
Sub-division :- Algae
Class :- Chlorophyceae
Order :- Chaetophorales
Family :- Coleochaetaceae
Genus :- Coleochaete

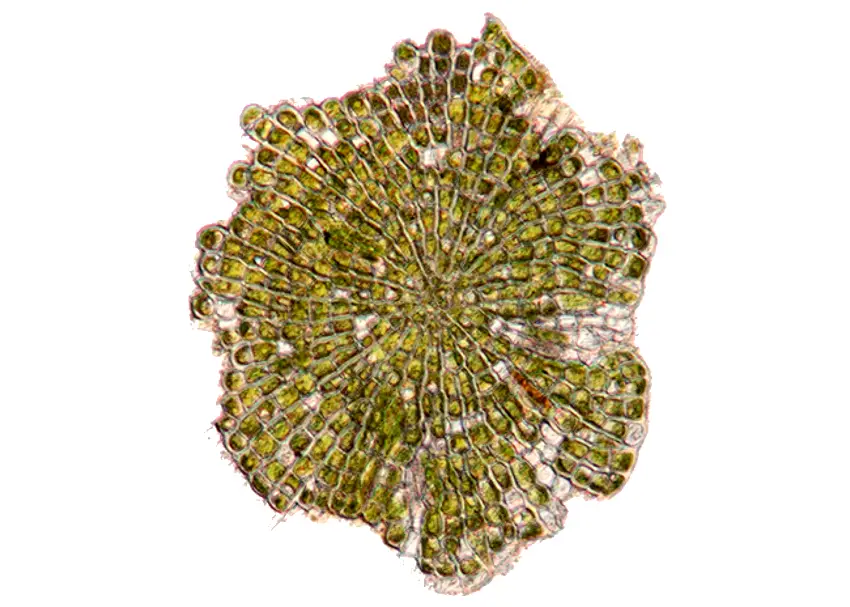
THALLUS OF COLEOCHAETE
- Thallus is multicellular and heterotrichous.
- It is either a disc-like structure ip. majority of the species (e.g. c. scutata) or cushionoid or filamentous (e.g. c. pulvinata) in others.
- It thallus is disc-like, the disc represents only the prostrate system while a few setae or hair, represent erect system.
- Filamentous thallus exhibits typical heterotrichous habit with a branched prostrate system and a branched projecting (erect) system.
- In both the cases a few cells possess a cytoplasmic outgrowth-setae. Setae are surrounded partly or wholly by a gelatinous sheath at the base.
- The thallus is distinctly enveloped by a gelatinous sheath or mucilage.
- In discoid species cells of the thallus are joined end to end to form branches. These branches are laterally apposed to one another to form a pseudoparenchymatous disc.
- Each cell is uninucleate. It has single, large, laminate and parietal chloroplast with a single pyrenoid. Rest of the cell is occupied by the cytoplasm.

REPRODUCTIVE STRUCTURES OF COLEOCHAETE

- Thalli may be homothallic or heterothallic.
- Sexual reproduction is oogamous.
- Antheridia are generally borne at the tips in filamentous species and in the middle or peripheral region in the discoid species.
- Anteridia appear as a group of small cells.
- Oogonia are also borne terminally in filamentous species and towards periphery in the discoid species.
- Oogonium is a flask-shaped structure with long tubular trichogyne.
- The fertilization results in the formation of a zygote which remains embedded inside the wall of the oogonium. It is a thick walled structure.
- Zygote known as spermocarp remains enveloped in a parenchymatous tissue formed by the development of neighbouring cells. It is conspicuously reddish-brown in colour.
- Spermocarp remains dormant for a long period.

IDENTIFICATION
- Sub-division– Algae
- Presence of a simple thallus.
- Chlorophyll present
- Cell wall made of cellulose.
- Class – Chlorophyceae
- Presence of a definite nucleus
- Chloroplast present. grass green colour
- Presence of starch
- Reproductive structure motile and flagella equal in length.
- Order – Chaetophorales
- Plant body heterotrichous
- Distinct prostrate and erect systems present.
- Presence of setae
- Family – Coleochaetaceae
- Vegetative cells with long cytoplasmic hair (setae).
- Cells uninucleate
- Filaments branched
- Each cell with a single parietal and laminate chloroplast.
- Genus – Coleochaete
- Plant body multicellular.
- Thallus parenchymatous
- Presence of spermocarp.

Leave a Reply