Contents
CHLAMYDOMONAS
CLASSIFICATION OF CHLAMYDOMONAS
Sub-division :- Algae
Class :- Chlorophyceae
Order :- Volvocales
Family :- Chlamydomonadaceae
Genus :- Chlamydomonas

GENERAL CHARATERSTICS OF CHLAMYDOMONAS
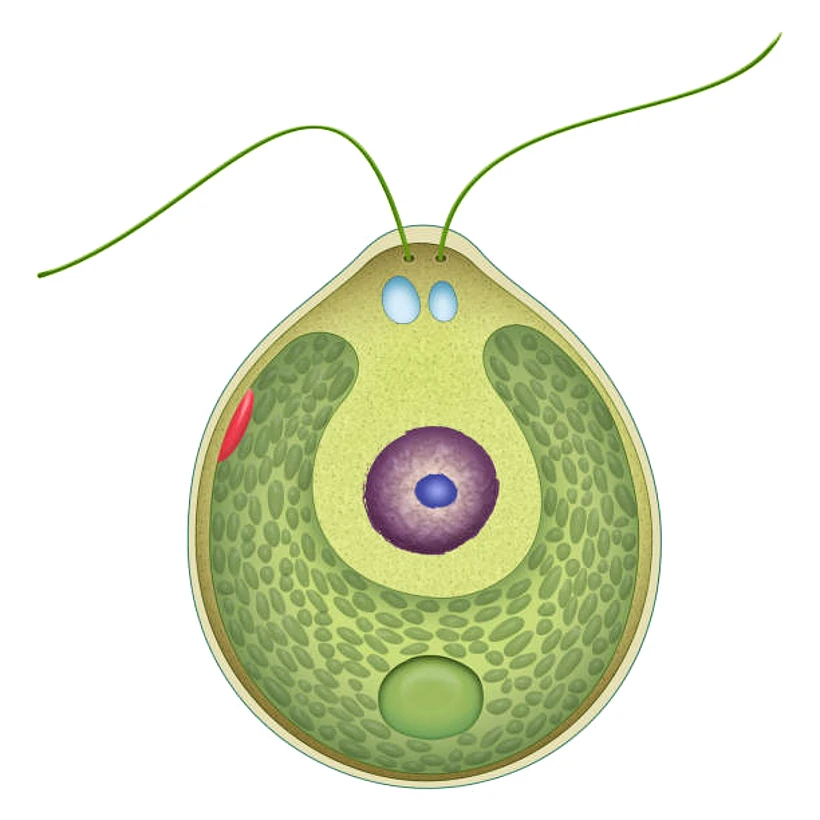
- Thallus is unicellular and motile.
- The cell is usually oval in shape. Sometimes spherical, oblong, pyriform or ellipsoidal.
- The cell is surrounded by a cell wall. It is narrow at its anterior end and broad at the posterior end.
- Anterior end bears two closely situated flagella (whiplash type).
- At the base of each flagellum lies a blepharoplast or basal granule.
- A small projection or papilla, known as apical papilla, is present in between the two anteriorly inserted flagella.
- At the base of each flagellum one contractile vacuole is present.
- Just near the cell wall, towards the anteriolateral part of the cell, lies an orange or red coloured spot, called stigma or eye spot.
- The broad posterior part has a large, massive and a single cup-shaped chloroplast. The thin sides of the chloroplast cup extend towards the anterior end.
- The broad portion of the chloroplast has a single pyrenoid (sometimes two to many).
- The cavity of the cup-shaped chloroplast is completely filled with the cytoplasm in which lies a single nucleus.
- Many volutin grains, the main reserve food product, are irregularly distributed in the cytoplasm.

IDENTIFICATION
- Sub-division– Algae
- Presence of a simple thallus.
- Chlorophyll present
- Cell wall made of cellulose.
- Class – Chlorophyceae
- Presence of a definite nucleus
- Chloroplast present. grass green colour
- Presence of starch
- Reproductive structure motile and flagella equal in length.
- Order – Volvocales
- Thallus motile,
- Protoplast with contractile vacuoles.
- Family – Chlamydomonadaceae
- Genus –Chlamydomonas
- Oval or pyriform shape of the thallus which is unicellular
- Cup-shaped chloroplast
- Presence of an eye spot
- Formation of Palmella stage.

Leave a Reply