Contents
CLASSIFICATION OF CERAMIUM
Sub-division :- Algae
Class :- Rhodophyceae
Sub class :- Florideae
Order :- Ceramiales
Family :- Ceramiaceae
Genus :- Ceramium
Ceramium occurs very commonly between tide levels and also in deeper waters. The species of the genus are especially abundant in Mediterranean coast. The commonest Indian species include Ceramium cruciatum, C. elegans, C. strictum, C. subdichotomum, etc.
EXTERNAL FEATURES OF THALLUS OF CERAMIUM

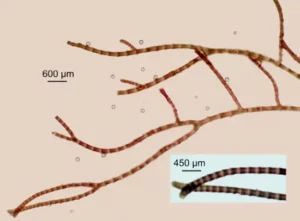
- The thallus is red or yellowish-green or redbrown in colour.
- The plant body is filamentous, uniaxial, multicellular and richly branched showing distinct bands.
- The filament is typically dichotomously branched. The apical region of the branches show characteristic tong-like forkings.
- The thallus is attached to the substratum by a cushion-like structure that produces rhizoids.
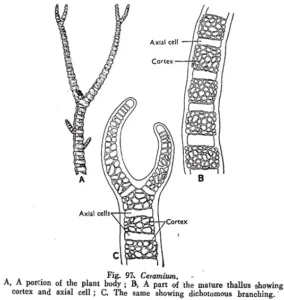
- The plant body is made of a single row of large cylindrical or barrel shaped cells (the axial cells) arranged one over the other.
- The banded appearance of the main filament is due to envelope of cortical cells (cortical filaments or branches) cut off by the axial cells.
- The cortical cells or branches are produced discontinuously. This results in alternation of corticated and non-corticated regions.
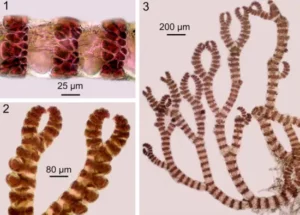
SPERMATANGIA – THE MALE SEX ORGANS OF CERAMIUM
- The spermatangia or antheridia are present in dense sori or clusters on the upper side of the lateral branchlets.
- Each antheridium is oblong to spherical in shape.
- It is unicellular and uninucleate structure.
- The entire contents develop into a single, uninucleate and non-motile spermatium or male cell.
CARPOGONIUM – THE FEMALE SEX ORGAN OF CERAMIUM
- Carpogonium is borne terminally on short lateral branch called carpogonial branch.
- The branch consists of a few cells, at the apex of which is a carpogonium. It is made of a basal swollen portion-the carpogonium, in which lies the female nucleus and the terminal long drawn out receptive organ called the trichogyne.
- Post fertilization developments result in the formation of phase called carposporophyte. It is dependent on the female gametophytic plant.
- The carposporophyte consists of gonimoblast filaments bearing carposporangia at the tips. Each carpogonium has only one carpospore.

TETRASPOROPHYTE, TETRASPORANGIUM AND TETRASPORES
- The external features of tetrasporophytic plant resemble that of the gametophyte. It is multicellular, uniaxial, filamentous, corticated and the apical portions are tong-forked.
- The plant shows the presence of tetrasporangia.
- Tetrasporangia are developed in clusters from the enlarged cells of the cortical bands.
- Tetrasporangia remain partly embedded in the cortical bands.
- Each tetrasporangium has four tetraspores. Each tetraspore is uninucleate and haploid. It germinates to produce a new gametophytic generation.
IDENTIFICATION OF CERAMIUM
- Sub-division– Algae
- Presence of a simple thallus.
- Chlorophyll present
- Cell wall made of cellulose.
- Class– Rhodophyceae
- Chromatophores pure red to dark purple.
- Photosynthetic reserve in floridoside.
- Male gametes are non-motile.
- Female reproductive organ with trichogyne.
- Post fertilization product is cystocarp
- Sub-class :- Florideae
- Thallus basically filamentous,
- Pit connections between sister cells.
- Cells with more than one chromatophore.
- Carpogonium highly specialised.
- Order– Ceramiales
- Thalli uniaxial or multiaxial.
- Filaments corticated, polysiphonous.
- Spermatangia in clusters.
- Presence of trichoblasts.
- Family – Ceramiaceae
- Axes corticated.
- Spermatangia developed on special determinate branchlets.
- Cystocarps naked
- Genus – Ceramium
- Thallus is richly branched, banded due
to discontinuous cortication. - Apical regions of the branches tong-forked.
- Repeated dichotomous branching
- Thallus is richly branched, banded due

REFERENCES :-

Leave a Reply